Japan (EN)
Select your region or country.
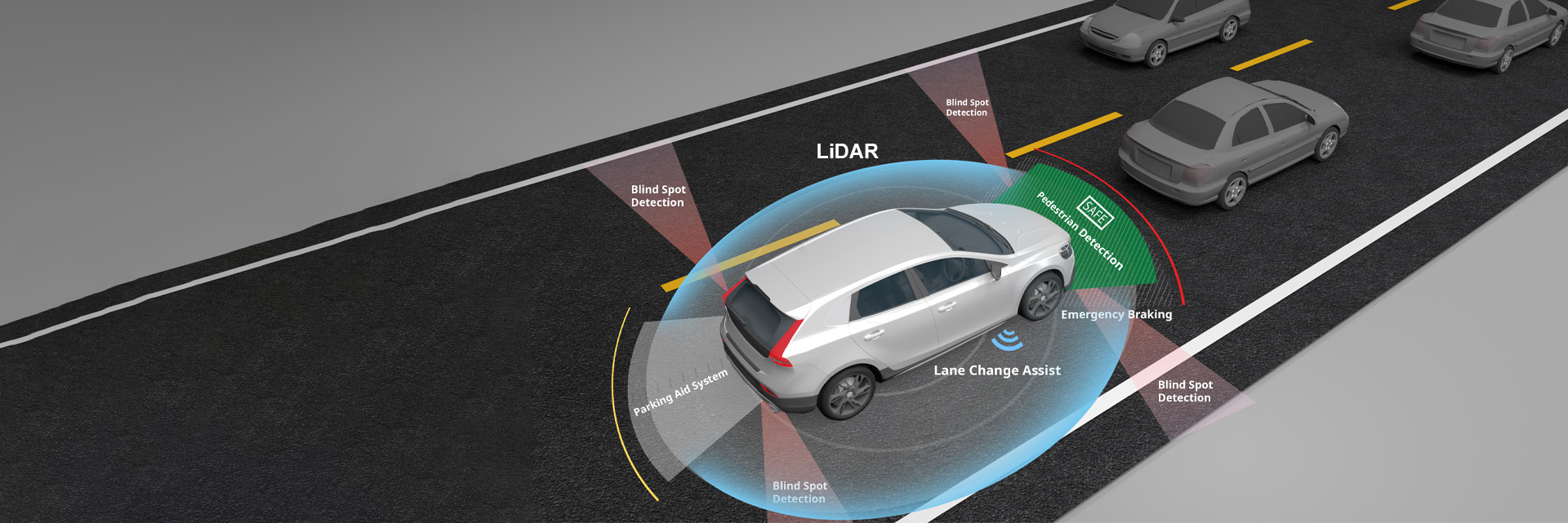
LiDAR for humanity
LiDAR for safety and productivity
LiDAR (light detection and ranging) uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure the range (distance) to a target by timing how long it takes for the light to travel to the target and reflect back to the sensor.
LiDAR is enabling technologies that better our lives, in everything from ADAS (advanced driver assistance systems), helping to reduce car accidents, to factory automation, overcoming workforce shortages and increasing productivity, to robo-taxis and trucking and robotic vacuums, improving the quality of everyday life.
ADAS technologies have the potential to prevent 20,841 deaths per year, or 62% of total traffic deaths. i
Application overview: LiDAR
LiDAR light-based remote sensing technology is an enabling technology to self-driving cars, but its promise is already improving passenger safety with ADAS safety features such as forward collision prevention, lane keeping assistance, blind spot detection and pedestrian automatic braking. By 2030, it is predicted that 20% of passenger cars sold will include LiDAR, rising to 57% by 2035. ii
LiDAR measures distance through time of flight (ToF) or coherent-based (i.e., FMCW) methods, both of which have their place depending on the application. In automotive LiDAR, ToF has been widely available for some time now, and found to be powerful, accurate, and affordable, though more improvements are being made to ensure accurate measurement in heavy rain, snow, and fog. Researchers are also pursuing various coherent LiDAR concepts such as FMCW and others; while these are still emerging methods facing challenges in cost, size and automotive compliance, their benefits such as better signal-to-noise ratio, better ambient light immunity and eye safety, and potentially better range have kept market interest in continued development of such concepts.
Photonics in LiDAR
LiDAR system developers are challenged to produce scalable, cost-effective solutions that operate in extreme temperatures and at a distance of up to 300 meters. ToF LiDAR systems measure distance by calculating the length of time for a light pulse to travel from its light source (laser), be reflected off an object, and return to a photosensor.
Hamamatsu provides light sources and photodetectors for short-range, mid-range and long-range ToF LiDAR; laser power and rotational angle monitoring photodetectors for ToF and coherent LiDAR concepts; as well as various components for LiDAR system calibration, manufacturing and testing.
Beyond the blog: more on automotive

Automotive
Hamamatsu delivers premium, reliable optical components, including LiDAR solutions, to advance vehicle safety, enhance comfort, and promote eco-friendly technologies. These innovations also support the efficient manufacturing and automation of critical automotive systems.
- Confirmation
-
It looks like you're in the . If this is not your location, please select the correct region or country below.
You're headed to Hamamatsu Photonics website for JP (English). If you want to view an other country's site, the optimized information will be provided by selecting options below.
In order to use this website comfortably, we use cookies. For cookie details please see our cookie policy.
- Cookie Policy
-
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in this cookie policy. By closing the cookie warning banner, scrolling the page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
Hamamatsu uses cookies in order to enhance your experience on our website and ensure that our website functions.
You can visit this page at any time to learn more about cookies, get the most up to date information on how we use cookies and manage your cookie settings. We will not use cookies for any purpose other than the ones stated, but please note that we reserve the right to update our cookies.
1. What are cookies?
For modern websites to work according to visitor’s expectations, they need to collect certain basic information about visitors. To do this, a site will create small text files which are placed on visitor’s devices (computer or mobile) - these files are known as cookies when you access a website. Cookies are used in order to make websites function and work efficiently. Cookies are uniquely assigned to each visitor and can only be read by a web server in the domain that issued the cookie to the visitor. Cookies cannot be used to run programs or deliver viruses to a visitor’s device.
Cookies do various jobs which make the visitor’s experience of the internet much smoother and more interactive. For instance, cookies are used to remember the visitor’s preferences on sites they visit often, to remember language preference and to help navigate between pages more efficiently. Much, though not all, of the data collected is anonymous, though some of it is designed to detect browsing patterns and approximate geographical location to improve the visitor experience.
Certain type of cookies may require the data subject’s consent before storing them on the computer.
2. What are the different types of cookies?
This website uses two types of cookies:
- First party cookies. For our website, the first party cookies are controlled and maintained by Hamamatsu. No other parties have access to these cookies.
- Third party cookies. These cookies are implemented by organizations outside Hamamatsu. We do not have access to the data in these cookies, but we use these cookies to improve the overall website experience.
3. How do we use cookies?
This website uses cookies for following purposes:
- Certain cookies are necessary for our website to function. These are strictly necessary cookies and are required to enable website access, support navigation or provide relevant content. These cookies direct you to the correct region or country, and support security and ecommerce. Strictly necessary cookies also enforce your privacy preferences. Without these strictly necessary cookies, much of our website will not function.
- Analytics cookies are used to track website usage. This data enables us to improve our website usability, performance and website administration. In our analytics cookies, we do not store any personal identifying information.
- Functionality cookies. These are used to recognize you when you return to our website. This enables us to personalize our content for you, greet you by name and remember your preferences (for example, your choice of language or region).
- These cookies record your visit to our website, the pages you have visited and the links you have followed. We will use this information to make our website and the advertising displayed on it more relevant to your interests. We may also share this information with third parties for this purpose.
Cookies help us help you. Through the use of cookies, we learn what is important to our visitors and we develop and enhance website content and functionality to support your experience. Much of our website can be accessed if cookies are disabled, however certain website functions may not work. And, we believe your current and future visits will be enhanced if cookies are enabled.
4. Which cookies do we use?
There are two ways to manage cookie preferences.
- You can set your cookie preferences on your device or in your browser.
- You can set your cookie preferences at the website level.
If you don’t want to receive cookies, you can modify your browser so that it notifies you when cookies are sent to it or you can refuse cookies altogether. You can also delete cookies that have already been set.
If you wish to restrict or block web browser cookies which are set on your device then you can do this through your browser settings; the Help function within your browser should tell you how. Alternatively, you may wish to visit www.aboutcookies.org, which contains comprehensive information on how to do this on a wide variety of desktop browsers.
5. What are Internet tags and how do we use them with cookies?
Occasionally, we may use internet tags (also known as action tags, single-pixel GIFs, clear GIFs, invisible GIFs and 1-by-1 GIFs) at this site and may deploy these tags/cookies through a third-party advertising partner or a web analytical service partner which may be located and store the respective information (including your IP-address) in a foreign country. These tags/cookies are placed on both online advertisements that bring users to this site and on different pages of this site. We use this technology to measure the visitors' responses to our sites and the effectiveness of our advertising campaigns (including how many times a page is opened and which information is consulted) as well as to evaluate your use of this website. The third-party partner or the web analytical service partner may be able to collect data about visitors to our and other sites because of these internet tags/cookies, may compose reports regarding the website’s activity for us and may provide further services which are related to the use of the website and the internet. They may provide such information to other parties if there is a legal requirement that they do so, or if they hire the other parties to process information on their behalf.
If you would like more information about web tags and cookies associated with on-line advertising or to opt-out of third-party collection of this information, please visit the Network Advertising Initiative website http://www.networkadvertising.org.
6. Analytics and Advertisement Cookies
We use third-party cookies (such as Google Analytics) to track visitors on our website, to get reports about how visitors use the website and to inform, optimize and serve ads based on someone's past visits to our website.
You may opt-out of Google Analytics cookies by the websites provided by Google:
https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout?hl=en
As provided in this Privacy Policy (Article 5), you can learn more about opt-out cookies by the website provided by Network Advertising Initiative:
http://www.networkadvertising.org
We inform you that in such case you will not be able to wholly use all functions of our website.
Close




